Dr. Nam Min-ho of KIST “Identifying Core Mechanisms…Applicable to Diagnosis and Treatment”,
,
, ‘(Seoul=Yonhap News) By Lee Ju-young = Domestic researchers have discovered that neuropathic pain, which causes severe pain even with mild stimuli, is due to the overproduction and secretion of the neurotransmitter GABA by non-neuronal reactive astrocytes in the spinal cord.’,
,
,
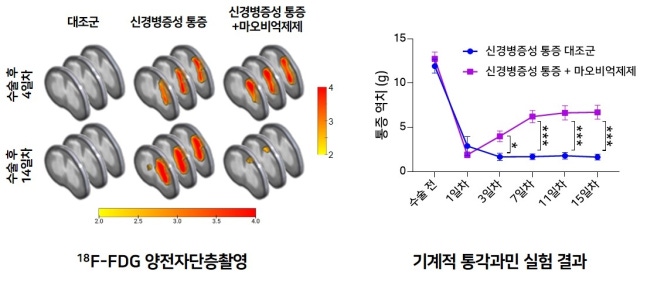
Therapeutic effect of neuropathic pain by monoamine oxidase B (MAOB) inhibitor
When administering a drug that inhibits MAOB, the key enzyme that generates GABA in a neuropathic pain model mouse, the ‘tonic excitation’ of nerve cells is inhibited within 2 weeks, as confirmed by positron emission tomography (PET) showing that glucose metabolism returns to normal levels (left). Also, mechanical allodynia measurements showed that administering MAOB inhibitors significantly restored pain thresholds in the neuropathic pain model within 1-2 weeks. [Provided by Korea Institute of Science and Technology. Redistribution and reprinting prohibited],
,
, ‘Increased glucose metabolism was observed in the spinal cord of neuropathic pain model mice, and it was apparent that inhibiting monoamine oxidase B (MAOB), the key enzyme that generates GABA, restored spinal cord glucose metabolism to normal levels by preventing GABA production.’,
,
, ‘The research team expects that positron emission tomography using glucose will visually display the progression of treatment, aiding in the prognosis management of neuropathic pain patients.’,
,
, ‘Furthermore, clinical trials are planned not only for the application of MAOB inhibitors being used in ongoing treatments for diseases like Parkinson’s, but also for securing the therapeutic effects and safety of neuropathic pain treatment.’,
,
, ‘Dr. Nam Min-ho stated, “Sustained excitation caused by GABA secretion in astrocytes is the cause of spinal cord neuronal hyperexcitability and the core mechanism of neuropathic pain,” adding, “These results will provide a crucial foundation for the development of new treatment strategies for neuropathic pain.”‘,
,
, “This research result has been published in the latest issue of the international academic journal ‘Experimental & Molecular Medicine.'”,
,
, ‘[email protected]’,
,
,

