All Indices for Value Added, Employment, and Job Creation Increase,

(Seoul=Yonhap News) Reporter Shin Ho-kyung = In 2023, the proportion of services in the Korean economy increased while the proportion of manufactured goods decreased. Due to declines in raw material prices, dependency on trade also reduced.
According to the ‘Input-Output Tables’ released by the Bank of Korea on the 24th, out of the total supply (total demand) of goods and services amounting to 6,802 trillion and 7 billion won in 2023, 29.6% accounted for foreign transactions, which is a sum of exports and imports. This proportion decreased by 1.9 percentage points from 31.5% in 2022.
Bu Sang-don, the head of the input-output team at the Bank of Korea, explained, “As the prices of imported raw materials decreased and exports of computers, electronics, and optical devices reduced, the proportion of foreign transactions in the economy also decreased.”
![Supply and Demand Structure [Provided by the Bank of Korea. Reproduction and DB prohibited]](https://imgnews.pstatic.net/image/001/2025/09/24/AKR20250924085100002_01_i_P4_20250924120122621.jpg?type=w860)
Examining the industrial structure, the share of manufactured goods in total output (value added + intermediate input) decreased from 42.8% to 41.2% within a year, focusing on basic materials such as coal and petroleum products. In contrast, the share of services increased from 46.8% to 48.1%, centered on professional, scientific, and technical services.
In terms of value-added criteria, manufactured goods decreased from 26.2% to 25.0%, but services increased from 65.1% to 65.4%.
![Composition of Total Output and Value Added [Provided by the Bank of Korea. Reproduction and DB prohibited]](https://imgnews.pstatic.net/image/001/2025/09/24/AKR20250924085100002_03_i_P4_20250924120122625.jpg?type=w860)
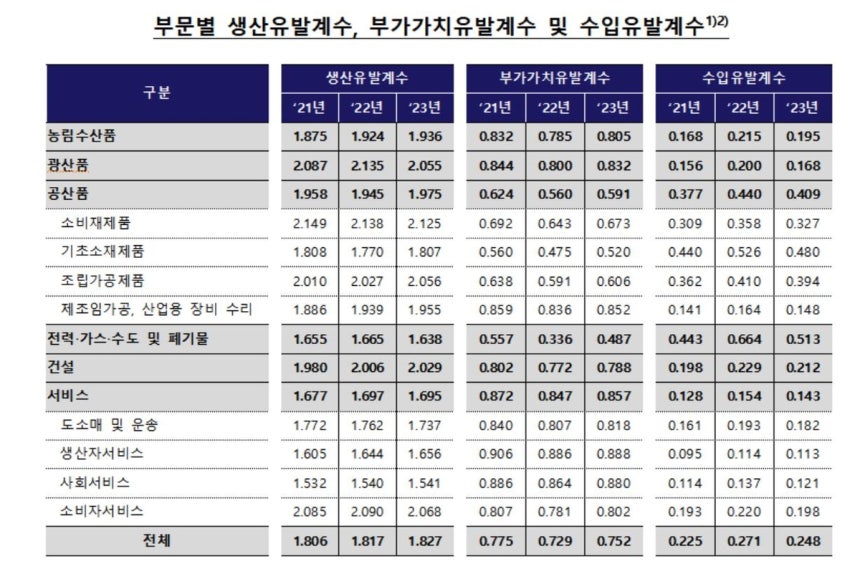
In 2023, the value-added inducement coefficient (0.752) increased from the previous year (0.729). The main influence was an increase in the value-added ratio (value added/total output) from 40.1% to 41.2%.
The production inducement coefficient also rose from 1.818 to 1.827. The Bank of Korea explained that this is related to the increase in the domestic intermediate input rate (the amount of domestic intermediate goods input/total input).
The value-added and production inducement coefficients refer to the size of value-added and production directly and indirectly triggered in all sectors, including those making the product, when a unit demand for a product occurs.
In 2023, the full-time equivalent (FTE) employment reached 25.99 million people, increasing by 560,000 people over a year. The FTE employment is a statistic calculated by converting the labor of part-time workers into the standard of full-time workers, including wage workers (permanent + temporary/day laborers), self-employed individuals, and unpaid family workers.
By employment type, the proportion of regular wage workers increased from 59.6% to 61.0%, whereas the day laborer proportion decreased from 15.4% to 14.5%.
By sector, the proportion of service employment increased from 71.1% to 71.7%, while employment in manufactured goods decreased by 0.3 percentage points to 14.5%.
Both the employment inducement coefficient (8.2 people) and job creation coefficient (6.2 people) increased compared to 2023 (8.1 people and 6.1 people, respectively).
The employment and job creation coefficients each refer to the number of employed persons and wage workers directly and indirectly triggered in all industries when a final demand of 1 billion won occurs.